Morocco, spring 2010 (April 19th to May, 11th) |
|
 |
|
| A little bit on Morocco: Topography, climate, zoogeography | |
| Morocco has a size of 460´000 square kilometres. It is about double size of Germany. Main part is the Moroccain Meseta, so called on its analogy to Central Spain. There is the most rich hydrography of all Maghreb countries. This plain is surrounded by the Atlas mountain ranges. In the north by the, up to 2´456 metres high Rif mountain ridge, the eastern border is formed by the Middle Atlas, reaching heights up to 3´340 metres. In the south there is the High Atlas, a mighty mountain range with altitudes up to 4´165 metres. The High Atlas is the highest mountain ridge in North Africa. South of the High Atlas runs, in an approx. parallel direction the Anti- or Saharian Atlas. This mountains have altitudes up to 2´531 metres above sea level. Between the last two mentioned mountain ranges are - in west-east direction - the Sous valley, the valleys of the rivers Draa and Dades and the Tafilalet." |
|
 |
|
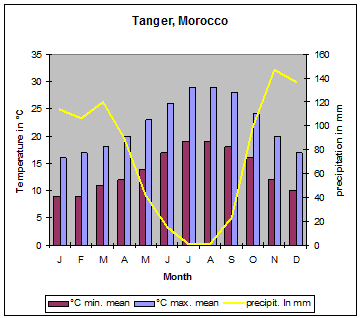
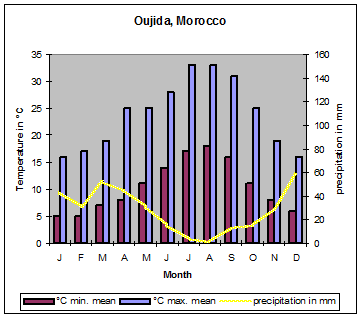
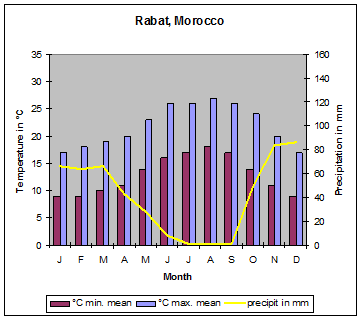
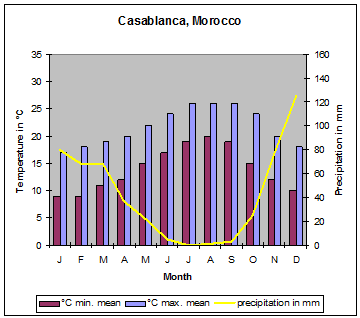
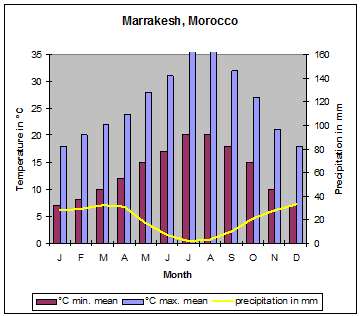
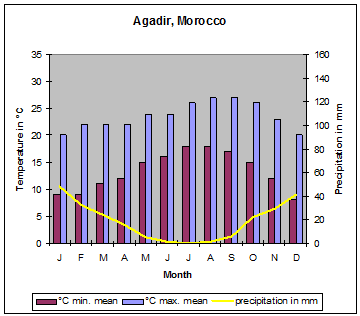
| Due to the mountain ranges mentioned above and shown on the map, Morocco has some different climate zones. Along the Mediterranean coast, south to the Rif mountains, mediterranean climate predominates. The Meseta has a dry and hot climate. At the northwest orientated slopes of the Atlas mountains orographic rainfalls cause precipitations up to 1´000 millimetres. During the winter month´ this precipitation changes to snow at altitudes of more than 1´000 metres. The areas south of the High Atlas have desert climate with very low or even missing precipitation." |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Due to the different clima zones and the barriers by the mountain ranges, areas have a different composition of Herpetofauna. Only a few species are distributed country wide, like, for example the Mauritanian Toad Bufo mauritanicus, the Stripeless Tree Frog Hyla meridionalis, the Spanish Terrapin Mauremys leprosa (this species occurs in different morphs, considered as own subspecies by some authors), Bibrons Agama Agama bibronii and the Viperine Snake Natrix maura. Restricted to the north, influenced by mediterranean climate are the Fire Salamander Salamandra algira, Manuel´s Skink Chalcides manueli and the Lataste´s Viper Vipera latastei. Typical representatives of the Saharian foreland with desert climate are among others the Desert Gecko Tarentola deserti, the Changeable Agama Trapelus mutabilis, the Desert Monitor Varanus griseus, Mograbin Diadem Snake Spalerosophis dolichospilus and the desert vipers of the Genus Cerastes. Some of these species are restricted to the open sandy areas Erg, like the Avicennaviper Cerastes vipera, others prefer the rocky desert (Hamada), like the Spiny Tail Agama Uromastix acanthinura. A few species are restricted to the higher elevations of the mountain ranges: Vipera monticola, Atlantolacerta andreanskyi and the Moroccain Day Geckos, Genus Quedenfeldtia. Along the Atlantic coast some subtropical and tropical reptiles reached Morocco, where they have their northwestern distribution limit in the Sous valley, like the Puff Adder Bitis arietans, the House Snake Lamprophis fuliginosus, the Egg-eating Snake Dasypeltis scabra and the Saw scaled Viper Echis leucogaster." |
|
You are here! | part 1 - Introduction: Topography, climate, zoogeography |
| part 2 - from Ceuta to Beni Mellal | |
| part 3 - from Beni Mellal to Marrakech | |
| part 4 - to Oukaimeden and from Marrakech to Ouarzazate | |
| part 5 - around Ouarzazate | |
| part 6 - from the Hammada(Ouarzazate) through the Reg(Tineghir) to the Erg(Merzouga)" | |
| part 7 - in and around the sand dunes (Merzouga and adjected areas) | |
| part 8 - From Merzouga to Taroudant in the Souss valley | |
| part 9 - western part of the Souss valley and south to the Tiznit area | |
| part 10 - home along the Atlantic coast, list of observed Amphibians, reptiles and birds | |